1. Introduction to Industrial Boilers
1.1 What is an Industrial Boiler?
An industrial boiler (also known as a steam boiler) is an essential industrial heating device, responsible for generating steam or saturated steam to serve production activities. The thermal energy in the boiler is created from burning fuel (coal, oil, gas, biomass) or using electricity (electric industrial boilers).
The steam produced from the boiler is distributed throughout the factory to:
- Provide thermal energy for production lines.
- Heating, drying, sterilizing, or operating machinery.
- Ensure stable operation for many industries.
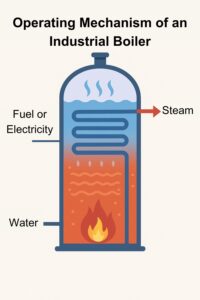
1.2 Operating Mechanism of Industrial Boilers
The operating mechanism of an industrial boiler can be simply visualized as follows:
- Fuel or electricity is supplied to the boiler.
- The generated heat is transferred to the water in the steam-generating chamber.
- Water is boiled and converted into high-pressure steam.
- The steam is directed through a piping system to supply the production line.
Practical Example:
In a textile factory, steam from an industrial boiler is used to heat the dyeing machines. Without a stable steam supply, the dyeing process cannot achieve accurate colors, which affects product quality.
1.3 Common Applications in Industries
Industrial boilers play a key role in many sectors:
- Food & Beverage: sterilization, cooking, distillation.
- Pharmaceuticals: sterilizing equipment, production temperature control.
- Chemicals: maintaining pressure and temperature in chemical reactions.
- Textiles & Dyeing: fabric dyeing, drying.
- Industrial Laundry & Hotels: supplying steam for laundry and drying systems.
Because of this wide range of applications, choosing the right industrial boiler becomes a decisive factor for operational efficiency.
2. Key Criteria for Choosing an Industrial Boiler
2.1 Efficiency and Energy Consumption
A high-efficiency industrial boiler will save fuel and reduce operating costs. Low efficiency leads to fuel waste and increased production costs.
2.2 Fuel and Boiler Type
- Coal/oil/gas-fired boilers: suitable for factories with available fuel sources.
- Electric industrial boilers: safe, clean, low emissions, suitable for the food and pharmaceutical industries.
2.3 Safety Standards and Inspection
Boilers are high-pressure equipment, so they must strictly comply with technical & safety standards (TCVN, JIS, EN). Installing cheap, non-standard boilers may pose risks of fire and explosion.
2.4 Maintenance Costs and Lifespan
A high-quality industrial boiler usually comes with a longer lifespan, fewer breakdowns, and lower maintenance costs.
2.5 Environmental Compliance
According to 2025 trends, the Vietnamese government encourages the use of environmentally friendly production equipment. Electric industrial boilers or biomass boilers are increasingly prioritized.

3. Advantages and Disadvantages of Choosing Cheap Industrial Boilers
In an increasingly competitive market, many businesses – especially newly established companies or small and medium-sized factories – tend to choose cheap industrial boilers to save on initial investment costs. However, whether “cheap” truly brings long-term benefits needs to be analyzed from both perspectives: advantages and disadvantages.
3.1 Advantages of Cheap Industrial Boilers
- Low Initial Investment Cost
This is the biggest advantage. A cheap boiler can cost only 60–70% of a standard-compliant unit. For small businesses, reducing initial capital pressure is crucial to quickly launching projects.
Example: A newly established industrial laundry workshop may choose a cheap boiler to meet basic needs instead of making a large upfront investment. - Easy to Purchase and Install
Cheap boilers often have a simple structure, requiring less advanced technical expertise during installation. As a result, businesses can put the equipment into operation quickly without extensive infrastructure. This is especially useful for projects that need rapid deployment to meet production deadlines.
3.2 Disadvantages & Risks of Choosing Cheap Industrial Boilers
- Low Efficiency – Higher Long-Term Operating Costs
Although saving on initial purchase, cheap boilers usually operate 10–20% less efficiently than standard models. This means businesses must consume more fuel to produce the same amount of steam, increasing monthly fuel costs.
Example: A food factory using a low-efficiency boiler may spend hundreds of millions of VND more per year on fuel, far exceeding the initial savings from purchasing a cheap unit. - Poor Material Quality – Susceptible to Damage and Corrosion
Cheap boilers often use thin steel or components that do not meet international standards. This makes the equipment prone to corrosion, leakage, and cracking after a short period of operation. As a result, businesses incur additional repair or replacement costs. - Safety Risks
Boilers are high-pressure equipment. If not manufactured to standards, the risks of gas leaks or boiler explosions are significant. Accidents not only cause property damage but also directly threaten worker health and lives, leading to legal liabilities and reputational damage. - Short Lifespan – Costly Replacement
Typically, a high-quality industrial boiler can run reliably for 15–20 years with proper maintenance. In contrast, cheap boilers may last only 3–5 years before severe degradation forces replacement. The total lifecycle cost is therefore much higher than the initial low-cost choice. - Difficult to Meet Environmental Standards – Risk of Penalties
Vietnam and many countries are tightening regulations on emissions and environmental safety standards. Cheap boilers often fail to meet these requirements, exposing businesses to regulatory penalties or even operational suspension. This is particularly dangerous for exporters, as international clients demand strict compliance.
3.3 Should You Choose a Cheap Boiler?
Clearly, while low-cost boilers provide short-term capital relief, the risks in operation, safety, long-term costs, and environmental compliance are substantial. Cheap boilers should only be considered for short-term, small-scale projects with minimal steam quality and safety requirements.
For industries with strict demands such as food, beverages, pharmaceuticals, textiles, chemicals, or hospitality, choosing a cheap boiler almost certainly results in higher long-term costs and potential legal and reputational risks.
Businesses need to carefully evaluate the total cost of ownership (TCO) and prioritize efficiency – safety – durability instead of focusing only on the initial purchase price.
4. Electric Industrial Boilers – A Safe and Green Alternative
Given the limitations and risks of choosing cheap industrial boilers, many businesses are seeking safer, long-term, and environmentally friendly solutions. In this context, electric industrial boilers are emerging as a suitable alternative, especially for food, pharmaceutical, hospitality, and clean production industries.
4.1 Characteristics of Electric Industrial Boilers
- Use electricity to generate steam, eliminating fossil fuels.
- Quiet operation, no smoke or dust emissions.
- Easy to install in limited spaces.
4.2 Key Advantages
- Safer as there is no risk of gas leaks or explosions.
- Clean and eco-friendly, meeting strict requirements of the food & pharmaceutical industries.
- Low maintenance costs due to fewer mechanical components.
4.3 Disadvantages
- Electricity costs can be high if not optimized.
- Better suited for medium and small capacities.
5. Long-Term Cost Analysis of Investing in Industrial Boilers
When choosing a boiler, many businesses focus only on the initial purchase price while overlooking a more important factor: the total cost of ownership (TCO). This metric truly reflects investment efficiency and long-term impacts on cash flow and production performance.
5.1 Total Cost of Ownership (TCO)
The TCO of an industrial boiler includes many factors beyond just the equipment price:
5.1.1 Annual Fuel Costs
- This is the largest portion of boiler operating costs.
- With a low-efficiency boiler, businesses must burn more fuel to generate the same amount of steam → higher monthly costs.
5.1.2 Maintenance & Repair Costs
- Industrial boilers are high-pressure equipment that require regular maintenance.
- If buying a cheap boiler with poor-quality components, the costs of parts replacement and breakdown repairs will increase significantly.
5.1.3 Safety and Environmental Compliance Costs
- Factories must comply with emission standards, pressure inspections, and occupational safety certifications.
- A low-quality boiler may fail inspections, forcing businesses to make extra investments or risk penalties.
5.1.4 Downtime Costs in Case of Failure
- This is a “hidden cost” but extremely important.
- When a boiler breaks down, the entire production line is disrupted. In industries such as food or textiles, even a few hours of downtime can cause major losses from defective products, delayed contracts, and reputational damage.
Therefore, calculating TCO helps businesses look beyond the initial low price and make accurate investment decisions.
5.2 Practical Comparison
5.2.1 Cheap Boilers
- Advantages: Low initial investment, easy deployment.
- Disadvantages:
- Low efficiency → higher fuel consumption.
- Prone to breakdowns, frequent repairs needed.
- Short lifespan (3–5 years).
- Consequence: The total cost after 5–7 years may exceed 1.5–2 times the initial purchase price, negating the “cheap” advantage.
5.2.2 High-Efficiency Boilers or Electric Industrial Boilers
- Advantages:
- High steam generation efficiency, saving 15–30% in fuel costs.
- Long lifespan (15–20 years).
- Fewer breakdowns, lower maintenance costs.
- Easier compliance with safety and environmental standards.
- Disadvantage: Initial investment cost is about 20–30% higher.
- Consequence: Over the equipment lifecycle, businesses save billions of VND thanks to reduced fuel costs, minimized downtime, and lower repair expenses.
5.3 The Importance of Long-Term Investment
An investment decision in industrial boilers not only affects production costs but also impacts the competitive capacity of the business.
- Short term: Low-cost units help reduce initial capital investment.
- Long term: High-quality boilers, especially electric industrial boilers, ensure stable operations, cost savings, compliance, and improved reputation with clients.
Therefore, instead of focusing on low initial prices, businesses should focus on long-term value, thoroughly evaluating TCO to make smart investment strategies.
6. Conclusion
It is clear that choosing cheap industrial boilers is only suitable for short-term, small-scale needs with minimal steam quality and safety requirements. Conversely, for businesses in industries such as food, beverages, pharmaceuticals, textiles, or hospitality – where production standards, safety, and environmental compliance are top priorities – the “cheap” option carries significant long-term risks and hidden costs. Therefore, businesses should prioritize high-efficiency, durable boilers that meet technical standards, and even consider environmentally friendly alternatives such as electric or biomass boilers. More importantly, select a reputable supplier capable of providing consultation and ongoing support in operation, maintenance, and warranty.
Maruse Engineering is ready to deliver optimal, safe, and efficient boiler solutions to help your business achieve sustainable long-term growth.