1. The Role of Industrial Electric Boilers in the Pharmaceutical Industry
1.1. Characteristics of the Pharmaceutical Industry and the Need for Clean Steam
The pharmaceutical industry is particularly sensitive, requiring extremely strict production conditions to ensure the purity, safety, and stability of final products. In this context, steam is not only a source of heat but also directly participates in production processes, acting as a technical agent.
Specifically, steam is used for:
- Sterilization of tools, equipment, test tubes, and tanks, eliminating harmful microorganisms without using chemicals
- Distillation of medicinal materials and essential oils – requiring stable temperature steam free of impurities
- Active ingredient extraction in pharmaceutical production, needing consistent heat and stable pressure
- Cleaning & sanitation of production systems, helping factories meet GMP/ISO standards
Therefore, steam quality must meet the following criteria:
- Colorless, odorless, impurity-free
- Stable temperature & pressure
- Free from oil, heavy metals, or bacteria
This is why pharmaceutical plants often prioritize using industrial electric boilers over fuel-fired boilers.
1.2. Advantages of Industrial Electric Boilers
Compared to oil- or coal-fired industrial boilers, electric boilers are increasingly preferred in pharmaceuticals thanks to the following advantages:
- Absolutely clean operation: No CO2, NOx, SOx emissions; no smoke, no dust – ideal for sterile environments such as cleanrooms
- Quick start-up: Direct electric heating generates steam within minutes, reducing waiting time
- Precise control: Integrated intelligent temperature and pressure controllers ensure uniform heat, avoiding fluctuations that affect pharmaceuticals
- Lower maintenance costs: No combustion chamber, fewer mechanical parts, less wear and tear, reduced repair frequency
- Easy automation integration: Compatible with PLC, SCADA systems – supporting automated GMP/GLP-compliant production lines
Additionally, electric boilers save space, operate quietly, and can be installed directly in production workshops without separate boiler houses like fuel-fired units.
1.3. Typical Application Segments
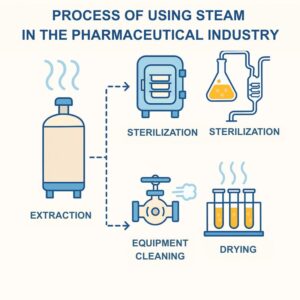
In practice, industrial electric boilers are applied across various pharmaceutical plant processes, from production to sanitation:
- Equipment sterilization: Using saturated steam to disinfect instruments, test tubes, and tanks – ensuring sterility before entering production lines
- Pharmaceutical production: Steam provides heat for extraction, concentration, and distillation of raw materials – especially natural herbs, essential oils, and intermediates
- Production line cleaning: Steam cleans pipelines, mixers, and tanks according to ISO/GMP without leaving chemical residues
- Drying raw materials: Indirect steam drying of herbs, tablets, and sensitive materials – precise humidity control prevents damage
These applications demonstrate that industrial electric boilers not only provide heat but also contribute to protecting pharmaceutical quality and ensuring compliance with international standards.
2. Mandatory Technical Standards for Using Electric Boilers in Pharmaceuticals
To ensure absolute safety for products and users, the pharmaceutical industry requires strict compliance not only with steam quality but also with technical regulations and safety standards for the system itself.
Industrial electric boilers, as the main heat-generating equipment for sterilization, extraction, cleaning, etc., must be strictly controlled from design to operation and maintenance.
Below are the key groups of technical and safety standards that all industrial boilers used in pharmaceuticals must follow:
2.1. Vietnamese & International Standards
The following standards are the legal and technical basis for the safe design, installation, and operation of industrial electric boilers:
- TCVN 7704:2007: Design, manufacture, operation & repair of industrial boilers
- TCVN 12728:2019: Safety technical requirements for pressure equipment
- ASME Section I (for export): International standard for industrial thermal equipment
These standards ensure that industrial thermal equipment such as electric boilers operate safely, efficiently, and legally.
2.2. Steam & Feedwater Quality
In pharmaceuticals, steam is not just a heat agent but also directly contacts active ingredients, tools, and equipment. Therefore, steam must meet “pharmaceutical clean” standards – similar to purified water.
Key technical parameters include:
- pH: 7.0 – 8.5
- Conductivity: < 1 μS/cm
- Free of chlorine, iron, copper, oil/grease
- Feedwater must be softened and demineralized
Non-compliant feedwater can cause scale, heating element corrosion, reduced heat transfer efficiency, and most importantly, steam contamination – directly affecting pharmaceutical quality.
>>> Related article: How to determine boiler capacity for industry
2.3. Inspection & Safety Requirements
Since boilers are high-pressure equipment, leaks or explosions can cause serious consequences, so inspection regulations are very strict:
- Inspection before commissioning and periodically every 1–2 years
- Equipped with safety valves, pressure gauges, emergency shutdown systems
- Regular hydrostatic testing for pressure resistance
Additionally, companies must maintain operation logs, inspection records, and comply fully with safety operation guidelines in TCVN and ASME.
3. Typical Technical Specifications in Pharmaceuticals
After selecting a suitable industrial boiler that meets standards and safety, the next concern for pharmaceutical companies is the technical configuration of the equipment.
Industrial electric boilers are not “one-size-fits-all” but must be designed according to production line requirements for capacity, pressure, and automation.
Below are the common technical specifications in pharmaceuticals – where steam must be clean, stable, and easy to control.
3.1. Capacity & Working Pressure
Electric boilers used in pharmaceuticals typically have the following ranges:
- Common capacity: 50 – 500 kg/h
- Working pressure: 0.7 – 10 bar
- Steam temperature: 170 – 180°C
These parameters suit sterilization and gentle drying of raw materials.
Steam pressure and temperature within these ranges suit light to medium pharmaceutical processes, preventing material damage or loss of active compounds.
3.2. Construction Materials
Pharmaceuticals demand high cleanliness, corrosion resistance, and easy maintenance – therefore, materials for industrial boilers must be carefully chosen:
- Boiler body: Stainless steel 304 or 316L – corrosion-resistant, easy to clean
- Heating elements: Special alloy, long lifespan
- Insulation layer: Ceramic fiber, retains heat, reduces energy loss
Using chemically- and heat-resistant materials not only extends boiler lifespan but also ensures steam quality remains clean and stable.
3.3. Automation Integration
Pharmaceutical production requires precise control, minimized human error, and stable 24/7 operation. Modern boilers therefore integrate automation systems:
- Water level, pressure, and temperature sensors
- Automatic feedwater system
- PLC or HMI control cabinets
Automation not only reduces operating costs but also increases accuracy, safety, and compliance with GMP/ISO throughout the production line.
>> Related article: 5 Common Industrial Boiler Failures and Solutions
4. Challenges & Solutions When Implementing Industrial Electric Boilers in the Pharmaceutical Industry
Despite outstanding advantages such as cleanliness, ease of operation, and precise control, industrial electric boilers still face certain challenges during installation and operation in pharmaceutical plants.
Identifying these issues early and proposing appropriate solutions from the outset is the key for businesses to operate stably, save costs, and ensure production quality.
4.1. High operating costs without optimization
Challenge:
Compared to oil- or gas-fired boilers, industrial electric boilers use direct electricity, and power costs can account for a large proportion of total operating costs if:
- They run continuously even when not needed
- Capacity is oversized relative to actual demand
- There is no smart control system → leading to power waste
Solution:
- Carefully calculate steam demand by time slots and production lines to select appropriate capacity (e.g., use a 200 kg/h boiler instead of 500 kg/h if only light drying is required)
- Design a reasonable operating schedule: avoid “idle” (no-load) operation
- Apply automated control technologies: PLCs, inverters, and sensors to optimize electrical power
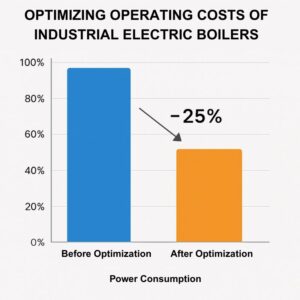
At present, Maruse offers flexible capacity customization and real-time, hour-based control to help businesses reduce electricity consumption by 10–25% each month
4.2. Ensuring feedwater quality
Challenge:
Non-compliant feedwater is the leading cause of:
- Scaling on heating elements, reducing heat transfer efficiency
- Corrosion of materials → causing leaks and early failure
- Steam contamination → affecting pharmaceutical quality
This is especially dangerous in pharmaceuticals, where steam must meet sterile, impurity-free standards.

Solution:
- Invest in a dedicated boiler water treatment system, including:
- Pre-filters: remove debris and particulates
- Water softener (removing Ca2+, Mg2+ ions)
- RO or DI system: demineralization and purification
- Periodically test feedwater quality (pH, conductivity, suspended solids)
Using standard-compliant water such as RO water helps extend heating element lifespan by 2–3 times, reduces failures, and saves on maintenance.
4.3. Compliance with pressure equipment safety
Challenge:
Industrial boilers are pressure equipment—if not properly controlled, they pose risks of fire and explosion, seriously impacting plant and personnel safety. Common issues include:
- No periodic inspection
- Lack of safety valves or pressure gauges
- Failure to keep complete operation records
Solution:
- Strictly comply with safety standards such as TCVN 7704, TCVN 12728, and ASME
- Perform initial & periodic inspections by authorized organizations (every 1–2 years)
- Install all required safety devices:
- Safety valves
- Pressure gauges
- Emergency power cut-off
- Maintain clear operation logs with signatures of responsible personnel for easy auditing
>>> Related article: Proper Industrial Boiler Maintenance
5. Advice for Selecting Industrial Electric Boilers for Pharmaceuticals
After understanding the role, technical standards, and implementation challenges, the final — yet extremely important — step is to choose the right type of industrial electric boiler tailored to pharmaceutical requirements.
Choosing incorrectly from the start (capacity, materials, supplier, etc.) not only incurs significant costs but also entails technical risks that affect product quality.
Below are three practical tips from the technical experts at Maruse Engineering to help you select the optimal boiler system for your pharmaceutical plant:
5.1. Prioritize steam quality & stability
In pharmaceutical manufacturing, steam quality directly affects process safety and effectiveness:
- Steam must be absolutely clean, free of oil/grease, heavy metals, or impurities that could contaminate products
- Steam must be stable in pressure and temperature to avoid fluctuations that impact extraction, sterilization, or drying
Electric boilers are ideal for processes requiring pure steam because they produce no exhaust emissions and are easy to control.
5.2. Choose the right capacity & materials
A common mistake is selecting boilers with capacities that are too large for actual needs — leading to:
- Higher monthly electricity costs
- Lower operating efficiency when the system runs under load
In addition, boiler construction materials should be carefully considered:
- Prioritize Stainless Steel 304 or 316L for the boiler body → corrosion resistance, durability, and suitability for clean environments
- Select energy-efficient, fast-heating elements that remain durable over time
Principle: “Adequate – clean – durable” are the three most important factors when choosing boilers for pharmaceuticals.
5.3. Partner with experienced providers
It’s not just the equipment — the supplier and installer also determine the long-term success of the system.
Maruse Engineering — with over 20 years of experience in industrial thermal equipment — is a trusted partner for many pharmaceutical companies, thanks to:
- Japanese-standard boiler solutions suitable for clean pharmaceutical production
- On-site technical consulting, real-world surveys, and optimized solutions for capacity & cost
- Official warranty and professional periodic maintenance services to keep systems stable and durable
“Good equipment + proper consulting + standard maintenance”, this is the formula for successful boiler operation in today’s pharmaceutical plants.
6. Conclusion
Industrial electric boilers are an ideal solution for the pharmaceutical industry — where clean steam, stable operation, and strict compliance with safety and technical standards are required. Choosing the right capacity, suitable materials, along with intelligent automation will help businesses cut costs, improve production efficiency, and ensure output quality. However, to implement successfully, companies must proactively control factors such as operating costs, feedwater quality, and inspection procedures for pressure equipment. Partnering with an experienced provider like Maruse Engineering will give you a properly designed, installed, and operated boiler solution tailored to pharmaceutical requirements — ensuring clean steam, high efficiency, and long-term safety for your production system.
Contact Maruse now for in-depth consultation and optimal solutions for your plant.